Blockchain - Opportunities of an emerging Technology in the Financial Industry
After several years of being relatively ignored by the financial sector, blockchain has gained popularity over the past year. The reason for this is simple - similar to the Internet, Blockchain does not yet bring directly implementable solutions, but it offers the basis for a wide range of applications. Since this potential of the Blockchain was discovered, a real race for the use of this new technology has broken out.
At this point, we would like to take a more strategic perspective in our publication. With an overview of how blockchain works, the areas of application, and the core aspects of its use, we offer a basis for discussion on the question of whether it is worthwhile to use blockchain in one's own company.
Your Opportunities
Currently, blockchain is a widely discussed technology. This attention is surely justified since blockchain provides several fields of application. Established systems can be improved regarding costs as well as process speed. At the same time blockchain enables completely new business models to be unlocked.
In the bigger picture, blockchain is not a selfsufficient, stand-alone system. Instead, it provides the infrastructure for applications and is yet to be adopted to every specific use-case. Therefore, there is not one unique blockchain, but rather a basic concept with adjustable parameters for the specific purpose.
The Technology
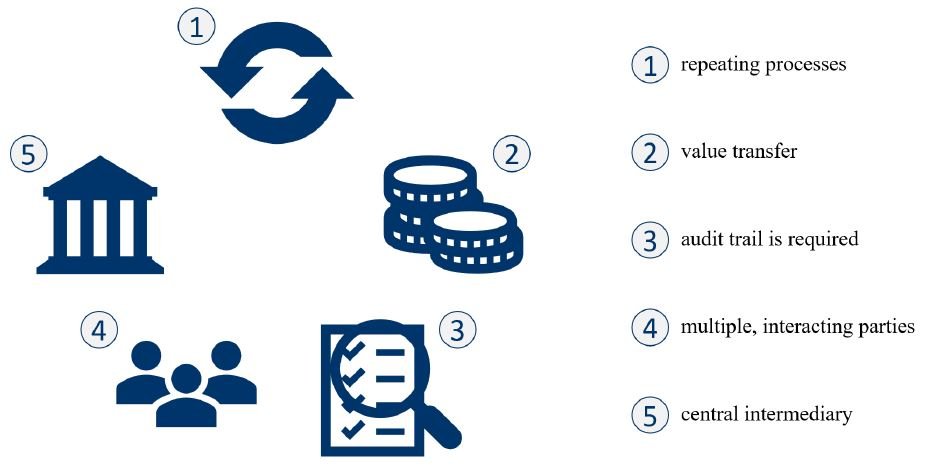
Putting it in a very simplified way, blockchain is a decentralised and among all participants distributed database. The information in this database is stored and intertwined in a way that makes entries irreversible. In this context the word blockchain is to be considered literally as chaining data blocks with the goal to prevent ex-post data manipulation. Figure 1 illustrates this process in a simplified way. New information is only added to an existing blockchain under the condition that the majority of participants agrees. Subsequently, the blockchain is monitored by the participants.
Figure 1: Blockchain’s Working Principle
One of the main features of blockchain is its absence of a central, controlling authority. The network of participating parties in its entirety assumes the responsibility for data validation. Therefore, every blockchain is based on the two following characteristic parameters.
Consensus Algorithm
The data validation by all participants requires a clear definition of every party’s voting rights in the process of the consensus. There are different algorithms for this purpose: Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake and the group of practical byzantine fault tolerance variants are the most important examples. Every algorithm has its own advantages and disadvantages, which can be narrowed down to the trade-off between corruption safety and computational effort. The proper consensus algorithm must be evaluated for every application depending on its requirements.
Private versus Public Blockchain
A blockchain can come in various levels of transparency. A permissionless blockchain allows every party to join the network. Data access as well as participation in the consensus algorithm is not restricted. In contrast to that, a permissioned blockchain offers possibilities to restrict participants and their rights. Doing so, the blockchain network can be limited to a certain number of known participants while data access can be either public or private.
The decision for the blockchain’s type varies with the particular application similar to the different consensus algorithms, since both types have their advantages and disadvantages.
Use cases
Generally speaking, blockchain offers the opportunity to revolutionise every process which involves an intermediary. Transferring the control functionality from one central party to the whole network provides high potential for optimization, especially regarding the financial industry.
Transactions can be directly settled between buy and sell side on the blockchain via self-executing code, so called smart contracts. This would make a central clearing party obsolete.
In the same way, Know-Your Customer processes could be structured as a direct push-mechanism, in which the financial institution asks the customer for access to information as opposed to the more resource-intensive practice of gathering the information themselves without the customer’s direct participation.
These two examples are solely intended to provide you with an idea of the wide-ranging possibilities for the application of blockchain. There are numerous use-cases, with a majority still remaining to be discovered. At this point, an early evaluation of potential fields of application for blockchain within your own business domain is highly valuable. Your position as an early-adopter could provide you with a significant competitive advantage, as it will allow you to position your business for sustainable growth at a time when disruptive FinTechs are entering the market aiming to replace established structures.
Our Consulting Approach
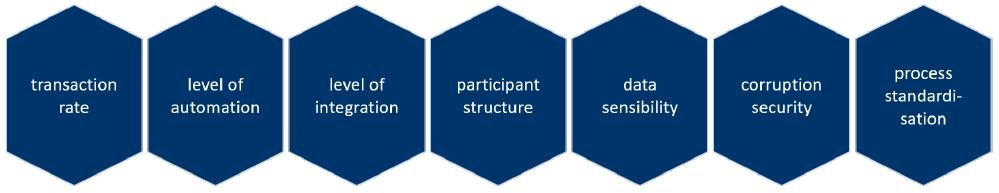
One point needs to be emphasised – blockchain is no panacea. As with every other technology, there are risks and issues which have to be considered carefully before applying blockchain. There are certain use-cases for which blockchain is highly beneficial. However, on the other hand there are other fields of application for which blockchain is simply not suitable. Therefore, early evaluation of the technology is even more important. A special focus should be put on application fields that meet a majority of the requirements stated in figure 2. Processes of this kind are predestined for blockchain application.
Figure 2: Selection Criteria for Blockchain Application
Besides the architecture and setup of a blockchain, comparing risks and benefits against each other and assessing the specific use-case is also another part of a holistic blockchain consulting approach. In taking such a comprehensive approach, we examine a set of certain, crucial factors. The participant structure must be defined. Identifying the intermediary is as important as a clear picture of the number of participants and their relation to each other. This also includes the definition of security and data protection aspects. The responses to arising questions like whether sensible data is affected or whether increased security is desired, fundamentally change the design of a blockchain system.
The advantages of the blockchain technology can only be fully utilized with a concept that is specifically tailored to meet the application’s requirements. Therefore, we consider a wide range of core aspects in a holistic analysis approach as shown in figure 3.
Figure 3: Core Aspects in Blockchain Consulting
Finbridge can help you in any blockchain related question, from conducting a preliminary study, developing a blockchain application, or integrating new blockchain systems into the existing IT architecture. Please do not hesitate to contact us.
About Finbridge
Finbridge is an independent specialised consultancy to financial services. With over 90 highly qualified consultants, Finbridge offers tailor-made implementation approaches throughout the entire process chain. Finbridge supports banks and financial services successfully in designing and implementing change processes resulting from new regulatory requirements, innovative financial products or adjustments to business models in risk controlling, regulatory reporting, trading and settlement.